Coatings in China: Present and Future
Market Demands Faster, Smarter, Stronger Products
Lacquer derived from tree sap originated in China about 7,000 years ago. This lacquer gave objects a hard protective coating that provided water resistance. Indeed, most of the early lacquer objects found in China reportedly come from flooded tombs. From these early origins, coatings in China have come a long way. In 2013, China accounted for slightly more than one-quarter of the total global coatings market, or about 13 million tons. For the years to 2020, the China National Coatings Industry Association forecasts an annual growth of 7%. This would result in a production volume of about 20 million tons in 2020.
Coatings Segments
In China, architectural coatings are by far the biggest segment, accounting for more than a third of total coatings volume (fig. 1).
Foreign-owned companies play a major role in the industry, accounting for about 50% of coatings sales. Relying on strong brands and technology, they traditionally focus on high-end coatings. In contrast, domestic companies (both state-owned and private) dominate the low end of the market. The middle level is the most interesting in terms of competition, with domestic companies entering from below via improved products and R&D, and multinationals entering via more localized products and corresponding cost and price level, often in combination with an acquisition of a local company.
Trends
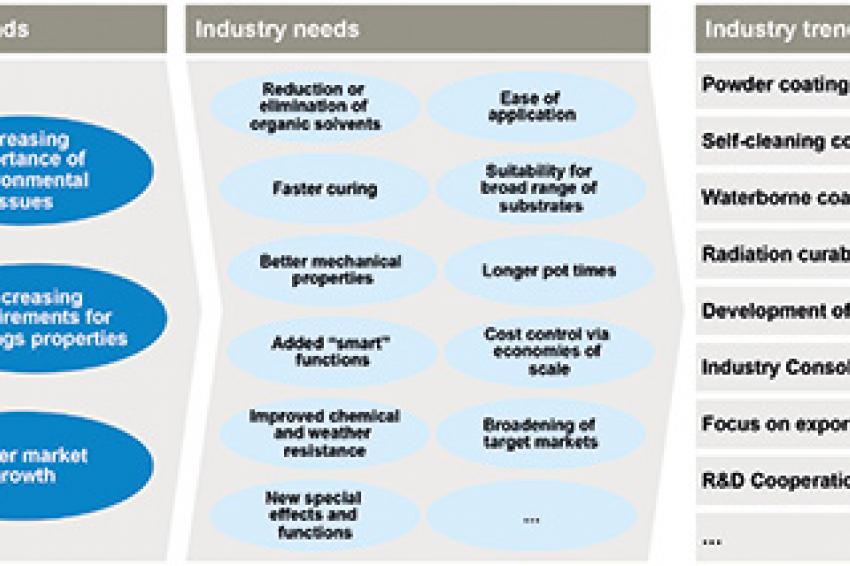
The coatings industry in China is undergoing more rapid changes than in more mature markets. Key drivers of these changes are three major market trends. The first is the move toward more environmentally friendly coatings in all phases of their life cycle from production to application, their useful lifetime and their final disposal. The second is the ever-increasing number of requirements for the functions and application properties of coatings. The third is the slower market growth in China (fig. 2).
Increasing importance of environmental issues: An improved environmental performance of China's coatings industry was a goal outlined in the 12th Five-Year Plan. The plan calls for a focus on the development of waterborne coatings, powder coatings, high solid coatings, radiation curable coatings and other environmentally friendly products. For example, the government goal was to increase the market share of waterborne coatings from 5% to 15% from 2011 to 2015, a goal that likely will be achieved. China thus follows the development in Western markets, where the replacement of solvent-borne coatings is already much more advanced.
Increasing requirements for coatings properties: As in the global market for coatings, customers continuously demand a higher level of performance and ease of application. In China, this effect is even more pronounced as the starting level of coatings properties is fairly low. Increased coatings requirements include the following:
- Faster application (e.g., single layer is sufficient)
- Faster curing times (particularly for industrial coatings)
- "Smart" properties such as self-cleaning, mold-preventing, etc.
- Photo catalytic properties (to destroy toxic chemicals)
- Improved resistance to chemicals, weather, etc.
- Lengthened intervals between reapplication
- Longer pot times
- New special effects (to allow differentiated branding, e.g., in aerospace coatings)
To achieve these properties, coatings companies engage in research and development. By now most major international coatings companies have some local research established in China. Domestic companies have also strengthened their R&D and are generally somewhat better at leveraging the coatings knowledge available at China's universities.
Slower market growth: The coatings industry has had a very good past decade with an annual growth rate of 18%. However, there is a need for some realism in preparing for the future. With China's growth likely to be in the range of 5%-7% in the upcoming years rather than 10%-12%, the overall coatings industry almost certainly will exhibit a similar reduction in growth. Even if some coatings segments keep growing much faster than gross domestic product, others will struggle to achieve just that. The coatings industry as a whole is simply too broad and too mature to grow at a very different rate from GDP. Overall, however, China's coatings market still grows fast compared with mature markets.
Risks
The overall Chinese coatings market covers a vast area of customer industries including both investment and consumer segments. The biggest risk for coatings manufacturers therefore is a significant slowdown of the economy.
Overcapacity is somewhat less of a risk in the coatings segment. This is mainly because capital investment on coatings production capacity is fairly low, and thus spare capacity will not necessarily lead to losses at coatings producers. However, overcapacity is a bigger threat for the producers of coatings raw materials, such as producers of resins, pigments and solvents.
Multinationals face increasing competition from local companies with a lower cost base and increasing product quality. They will have to reduce their cost base, particularly via localization of cost-intensive steps, and further localize their product development. Conversely, domestic producers need to be careful not to simply rely on low prices. For small domestic players, the route to success may be to focus on small, China-specific market niches. Large domestic players will need to further improve their product quality while retaining their cost advantage.
Opportunities
Markets: Most coatings producers currently do not cover all markets within their application segments. Multinational players thus have opportunities in expanding their product range at the lower end, while domestic companies can move further upmarket with more technologically advanced products.
Products: Coatings still have substantial room for development. The demand for environmentally friendly coatings will increase further, driven not only by government regulation but also by growing environmental and health concerns of end customers. The increased coatings requirements listed above offer many other opportunities for improved products.
Marketing: Most local brands are still fairly weak and require stronger branding efforts to compete with foreign brands. Conversely, multinational companies may consider establishing second brands in order to better target the medium and lower end of the market without diluting the brand image of their global high-end brands. In some segments, such as architectural coatings, marketing efforts will have to be somewhat redirected regionally, with the focus shifting from eastern to central and western China, and from first- and second-tier cities to third- and fourth-tier ones.
Service: In Europe, coatings producers are more active in providing services than in China, for example, by taking over complete coatings tasks instead of just providing materials. Producers in China may consider a similar approach. In addition, add-on services such as analytical services, vendor-managed inventory, financing, etc., may in the future become more widespread not only for coatings producers themselves, but also for their suppliers, e.g., the producers of solvents, resins, additives and pigments.
An Attractive Market
Despite the gradual slowdown of the Chinese economy, coatings in China are and will remain an attractive market. The many recent investments by both multinational and domestic companies show that this perception is widely shared. The coatings producers active in China will continue to expand their businesses, and will seek to actively improve their market position.
Contact
Managm. Consult. Chemicals
RM1302, 13/F CRE Bldg.
Wanchai, Hong Kong
China
+86 1368 1873992