European Chemical Industry Parks
25.09.2012 -
No Walk in the Park - European chemical industry parks and their operators face great challenges. On the one hand, they have to meet increased and more complex demands of globally active chemical companies. On the other hand, ongoing globalization leads to intensified competition among chemical industry parks that try to attract international investors. Clear strategic positioning, synergy-targeted infrastructure, and comprehensive and customer-oriented site services portfolios are basic requirements for future competitiveness.
Strategic positioning based on investors' key criteria combined with operational excellence in site operations is decisive. Chemical park operators have to contribute added value to the competitiveness of the chemical companies at the chemical park and, at the same time, have to organize their site operations in a customer-oriented, flexible and cost effective manner, defining their core competencies while outsourcing non-core services.
This is valid for both the European chemical industry parks with a high degree of integration and long production history as well as for the developing chemical production clusters in Southeast Asia, China and the Middle East that were designed on the drawing board after decade-oriented master plans.
Chemical industry parks gain competitive advantages by continuously orienting themselves toward key investment criteria of global chemical producers.
Focusing on the European chemical park operator landscape, four core questions have to be addressed:
- How can European chemical industry parks successfully position themselves in global competition for future investors?
- How can competitiveness of existing chemical sites be increased, in particular by regional cooperatives generating further synergies?
- What are the key competitive advantages of the considered European parks compared with the global peer group; which Unique Selling Points (USPs) could be proactively developed and which weaknesses of the park should be addressed?
- How could chemical industry parks continuously measure the investors' confidence and satisfaction for an ongoing site development?
Global Site Benchmarking Approach
Comparison with the world's leading chemical industry parks shows the own competitive situation. This approach, however, creates a value-add beyond grasping the gap to best-in-class peers. It guides to new ways of goal-oriented and sustainable site development, based on an extensive site benchmarking database that provides best practices, role models, site benchmarks and other valuable inside views into analyzed chemical sites in Europe, the U.S., China, Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
The benchmarking approach functions as facilitator to optimally apply instruments like best-in-class analysis per site success factor, strengths and weaknesses profiles, site service performance evaluations, structured collection of investors' feedback as in investor confidence surveys or more quantified cost structure analyses related to Costs of Goods Sold (COGS) or industry cost curves for specific production set-ups. It helps site operators to make the most effective and efficient investment decisions to further develop relative competitive advantages and to close identified gaps.
Evaluation Framework for Global Site Benchmarking
Based on defined site-success factors for high site competitiveness and attractiveness, chemical industry parks could be objectively evaluated from an investor's or existing resident's perspective. These site-success factors and the more than 70 underlying benchmarks are derived from companies' investment decision processes for new production sites and represent the first part of SCOPEIN's Global Site Benchmarking evaluation framework.
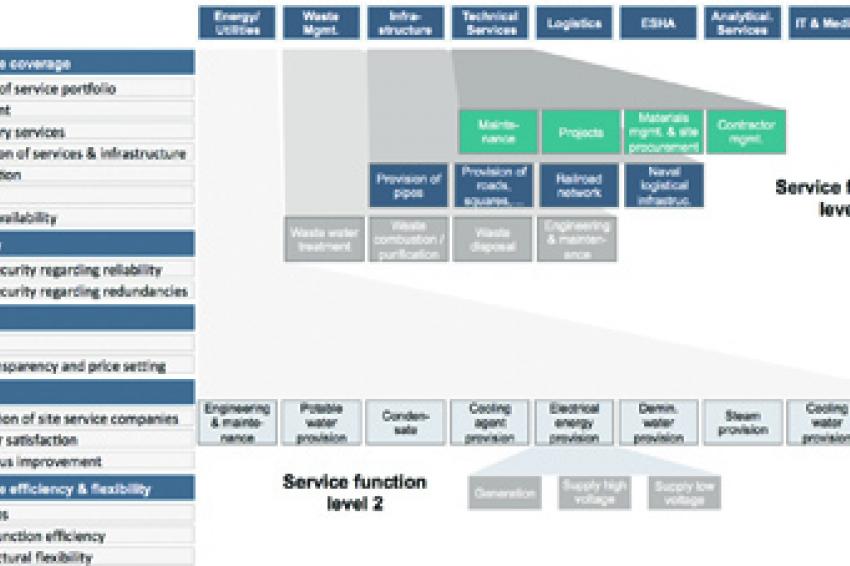
The second part consists of an assessment of the Site Service Performance, i.e. the site infrastructure and services available within the battery limits or nearby the site (figure 1).
The Site Service Performance evaluation is based on a holistic function model for chemical industry parks. All required site services and energies by the producing chemical companies are evaluated and analyzed applying criteria such as site service coverage, availability, price and cost level, quality as well as site service efficiency and flexibility (figure 2).
Insights into Global Site Benchmarking
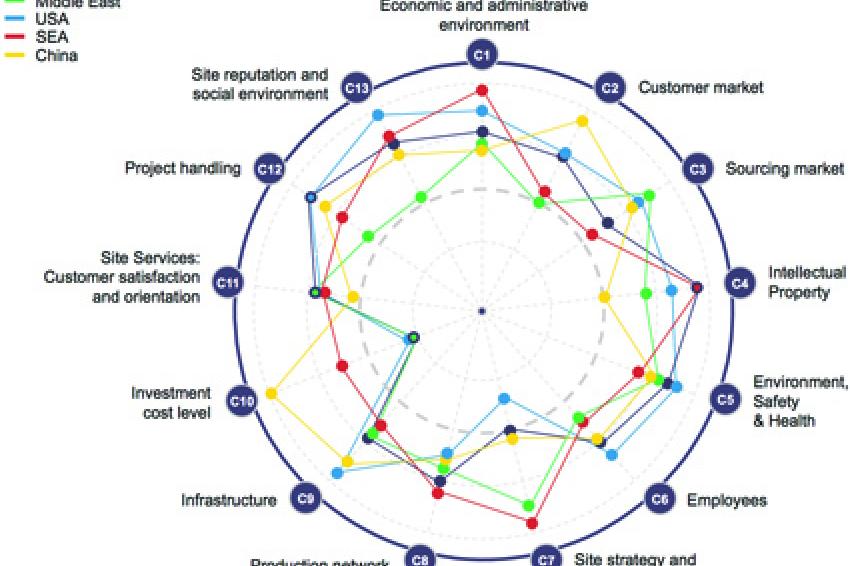
The most important and still valid conclusion drawn from benchmarking the worlds' leading chemical industry parks is that the "ideal chemical site for all kinds of investments with best-in-class chemical production conditions" does not exist. Instead, each site offers a portfolio of favorable and less favorable factors to be evaluated according to the projects' specific requirements. The challenge for globally operating chemical companies is to find the best-fit investment location facing the heterogeneity of chemical production locations. At the same time, it is an opportunity for chemical industry parks and their operators to present themselves at their best. The Global Site Benchmarking is key to both, identifying optimization levers for increased competitiveness for the own site and having a detailed and structured set of information regarding strengths and weaknesses of other worldwide leading chemical industry parks.
Figure 3 shows a global benchmarking comparison of chemical sites' success factors on top level.
Chemical Industry Parks in Europe
European chemical production sites provide very stable production conditions thanks to their long production history and highly professional site operators. Here, site service providers offer a very comprehensive site service portfolio and reliable infrastructure for chemical production companies according to the Plug & Play principle, leading to a high degree of customer satisfaction. A further main advantage of European sites is the availability of well-qualified personnel on all levels as well as reasonable Environment Safety and Health (ESH) regulations.
In general, investment cost levels are higher than at the Asian sites because of higher material, construction and engineering costs, but far lower than expected cost levels in the Middle East.
Chemical Industry Parks in the Middle East
Most Arabic states in the Middle East are actively looking for foreign investment and technology partners following their economic development strategies, among others the settling of downstream chemistry. Most chemical industry parks in the Middle East region are centrally managed and developed by governmental institutions or state companies that are specifically responsible for the construction and operation of basic infrastructure facilities (land provision). Large investment programs in world-class chemical site infrastructure, such as in Qatar, generate very favorable conditions for investments and operations. Concerning the economic and administrative conditions, foreign companies need a local sponsor to establish joint ventures that are characterized by a statutorily fixed share distribution among the partners.
The favorable logistical location in the Middle East between Europe and Asia and the availability of deep-water port access at major chemical sites are prerequisites to optimally serve the export-oriented chemical production, especially because of a very small local customer market. Cheap feedstock, access to the world's largest crude oil and natural gas reserves, good raw materials availability and cost levels as well as very favorable electrical energy prices compared with all other global sites are key investment advantages for the region.
Major challenges for investing companies are the limited availability of skilled labor and high investment cost induced by extreme climatic conditions. Special materials, technologies and maintenance services are required to achieve global utilization rates of the plants.
Chemical Industry Parks in the U.S.
In general, American chemical industry parks offer a very favorable environment for investments and operations of chemical plants. The cost situation regarding all major utilities such as electrical energy, steam and especially natural gas are at a world-class level. In addition, labor costs are approximately on the same level as in Europe, whereas labor productivity is very high in comparison with the rest of the world. When considering the economic and administrative environment, a rather high income tax up to 39.5%, due to high federal tax, has to be considered.
Chemical Industry Parks in Southeast Asia
Investments in chemical industry parks in Southeast Asia, especially in Jurong Island in Singapore, benefit from a world-class administrational environment that offers very favorable tax incentives and shows a very effective site commercialization and clearly defined site development strategy. Tax holidays up to 10 years and reduced income taxes could be highlighted. Site service provision and project handling are considered as advanced as the Asian sites, but do not always meet high European levels. Located close to one of the world's largest seaports, the region's leading chemical site Jurong Island is well connected to the global customer and sourcing markets. Major disadvantages are the electrical energy prices that are as high as at several chemical sites in Europe, e.g., chemical cluster Antwerp, but double the price of other Southeast Asian chemical sites. Concerning qualified employees, comparable to the Middle East and China, there is a strong need for internal company training on the job, because of missing dual education system. The German education system still functions as a role model for several initiatives started in Asia and elsewhere.
Chemical Industry Parks in China
Especially the large and dynamic customer market for chemicals as well as low investment and labor costs put Chinese chemical industry parks in a favorable position when compared with other sites. Labor cost levels amount to less than 10% to 20% compared with European sites. Nevertheless, intellectual property protection remains an issue in China, although legislation has been adjusted to international standards. Furthermore, the low degree of production integration at the considered sites is not really addressed by a proactive intercompany production network planning and site commercialization by the Chinese site operators. In addition, there are monopolistic structures of site services supply, however, in total they have no influence on favorable production costs for electrical energy, wastewater treatment or maintenance services.
Especially when considering more rural chemical sites compared with a very developed and professionally managed park like the Shanghai Chemical Industry Park, the sites are at very early stages of development in becoming a chemical park. The heterogeneity in the Chinese chemical sites' landscape is still extensive concerning, among other things, site strategies, production network development plans, availability of qualified labor, satisfying labor productivity level and site services as well as infrastructure provision.
Outlook
Continuous improvement of sites' competitiveness and attractiveness enable European chemical industry parks to be best prepared for increased competition for potential investors from investment locations in China, Southeast Asia and the Middle East. The identification of improvement and development potentials based on the defined site-success-factors model supports a targeted development of the individual park and the achievement of sustainable European sites' competitiveness.
Contact
SCOPEIN Management
Heinrich-Heine-Allee 53
40213 Düsseldorf
Germany